
How Do EV Charging Stations Work?
Electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a cleaner and more sustainable mode of transportation. In recent years, millions of people have switched to electric vehicles to reduce their carbon emissions and travel costs. As the demand for EVs continues to rise, the need for efficient charging infrastructure becomes increasingly important. EV charging stations play a crucial role in supporting the growth of the electric vehicle market. They also boost the confidence of EV owners in making the switch to electric vehicles. This blog will be your one-stop source for answering all your questions about how EV charging stations work, discussing the technology behind them, and the types of chargers available (AC & DC).
Understanding the Basics of EV Charging Station
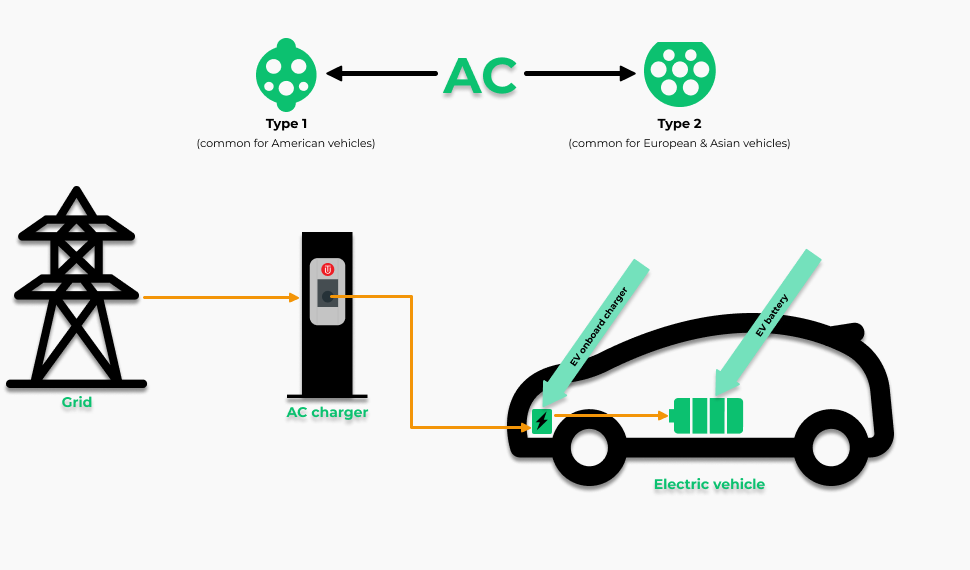
Electric vehicle charging stations, often referred to as EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment), are responsible for supplying electric energy to the batteries of electric vehicles. Let’s break down how they work in simpler terms:
Power Supply: Think of an electric vehicle charging station as a gas station for electric cars. It needs a source of electricity, just like a gas station needs a source of gasoline. This electricity usually comes from the regular electrical grid, the same place where your home gets its power. It’s like plugging in a giant extension cord to charge your car.
Conversion: The electricity that comes from the grid is like the power you use to run your TV or charge your phone at home. It’s called alternating current (AC). But most electric cars need direct current (DC) to charge their batteries. So, the EV charger has a special device inside it called a rectifier, which converts the AC electricity from the grid into DC that your car’s battery can use.
In simple terms, an electric vehicle charging station takes electricity from the grid, like a regular plug in your house, and transforms it into the kind of electricity your electric car’s battery can use.
Types of EV Charging Stations
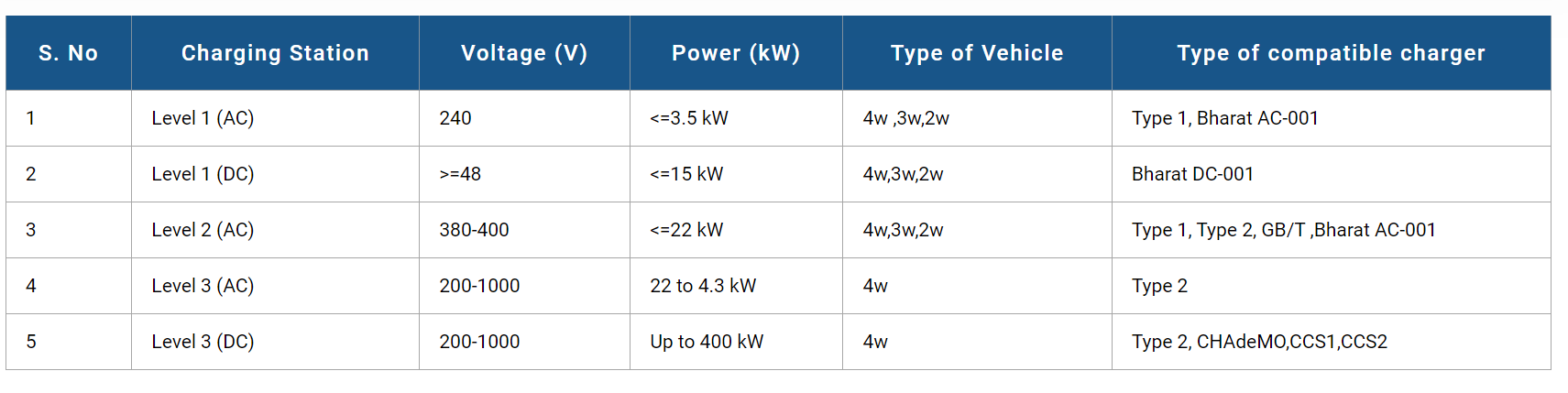
There are different types of charging stations available, each offering various charging speeds and applications:
- Level 1 Charging (240V AC): Level 1 chargers are the most basic and typically use a standard household outlet (240V AC). They provide a slow charging rate, suitable for overnight charging at home. However, they are not practical for fast charging on the go. Level 1 EV charging stations are typically used to charge 4-wheelers, 3-wheelers, and 2-wheelers, offering a power output <= 3.5 kW.
- Level 2 Charging (380-400V AC): Level 2 chargers are more powerful than Level 1 and use a 380-400V AC power supply. These are commonly installed at residential locations, workplaces, and public charging stations. Level 2 chargers offer faster charging speeds and are ideal for daily use. Level 2 EV charging stations are used to charge 4-wheelers, 3-wheelers, and 2-wheelers, offering a power output of <= 22 kW.
- Level 3 Charging (DC Fast): DC fast chargers supply direct current (DC) electricity directly to the vehicle’s battery, bypassing the need for onboard conversion. They are capable of delivering a significant amount of power and can charge an EV to 80% capacity in a relatively short time, making them suitable for long journeys and fast EV charging. DC Fast charging stations are used to charge 4-wheelers only, offering a power output of up to 400 kW.
Understanding the EV Charging Process
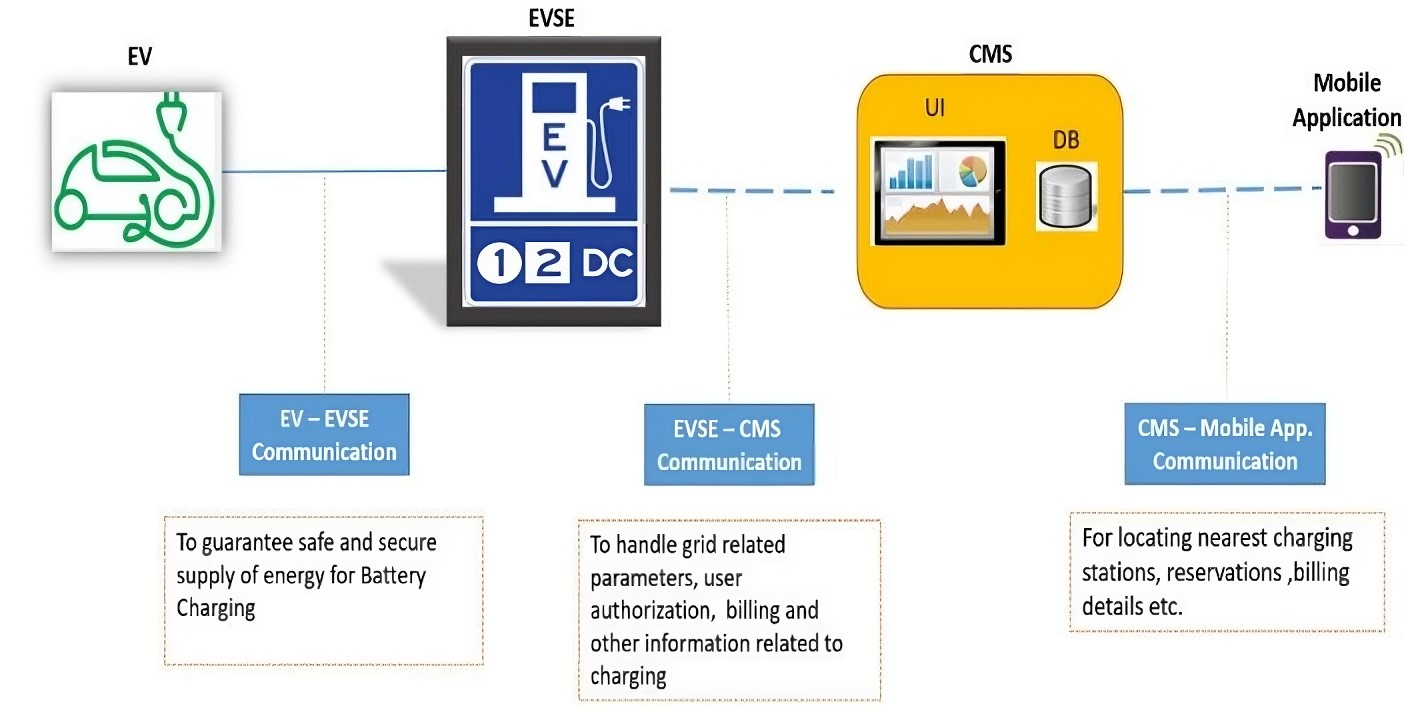
Once the vehicle and the EV charger at the charging station are connected, the charging process can begin. Here’s how it typically works:
- Authentication: Many charging stations require authentication, either through a physical card like RFID, a mobile app, or contactless payment such as Statiq Wallet. This ensures that only authorized users can access the charging station.
- Communication: The EV charger communicates with the electric vehicle to set the charging parameters, such as voltage, current, and charging rate. This ensures safe and efficient charging.
- Charging: The charging station supplies the appropriate voltage and current to the EV’s battery, which then stores the energy for later use. The charging progress is usually displayed on the charging station’s screen or through a mobile app.
- Autocut: EV chargers automatically turn off the charging once the battery reaches a predetermined state of charge, or it can also be manually stopped by the user. Safety mechanisms are in place to prevent overcharging and overheating.
Conclusion
EV charging stations play a vital role in enabling the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. They provide a convenient and efficient way to recharge an EV’s battery, whether at home, work, or on the road. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even faster charging speeds, increased compatibility, and more user-friendly features in the EV charging infrastructure.
Also Read, How Much Time Does It Take To Charge An Electric Vehicle?



